Batch Processing Product
Using our custom-built models and policies via batch processing can be accomplished in simple steps. Only getting familiar with the client-specific website and input data is required to get strategies for several of your customers at once. This guide takes a new Model Service user from login through using the deployed model to get results on an existing customer dataset.
There are 4 steps covered in this section for using our batch product:
- Login to the model service webpage
- Specify the appropriate model and input data
- Understand the input file
- Understand the output file
Step 1: Login to the model service webpage
As part of the onboarding process, 2OS will provide the client-specific website address, and sign in credentials.
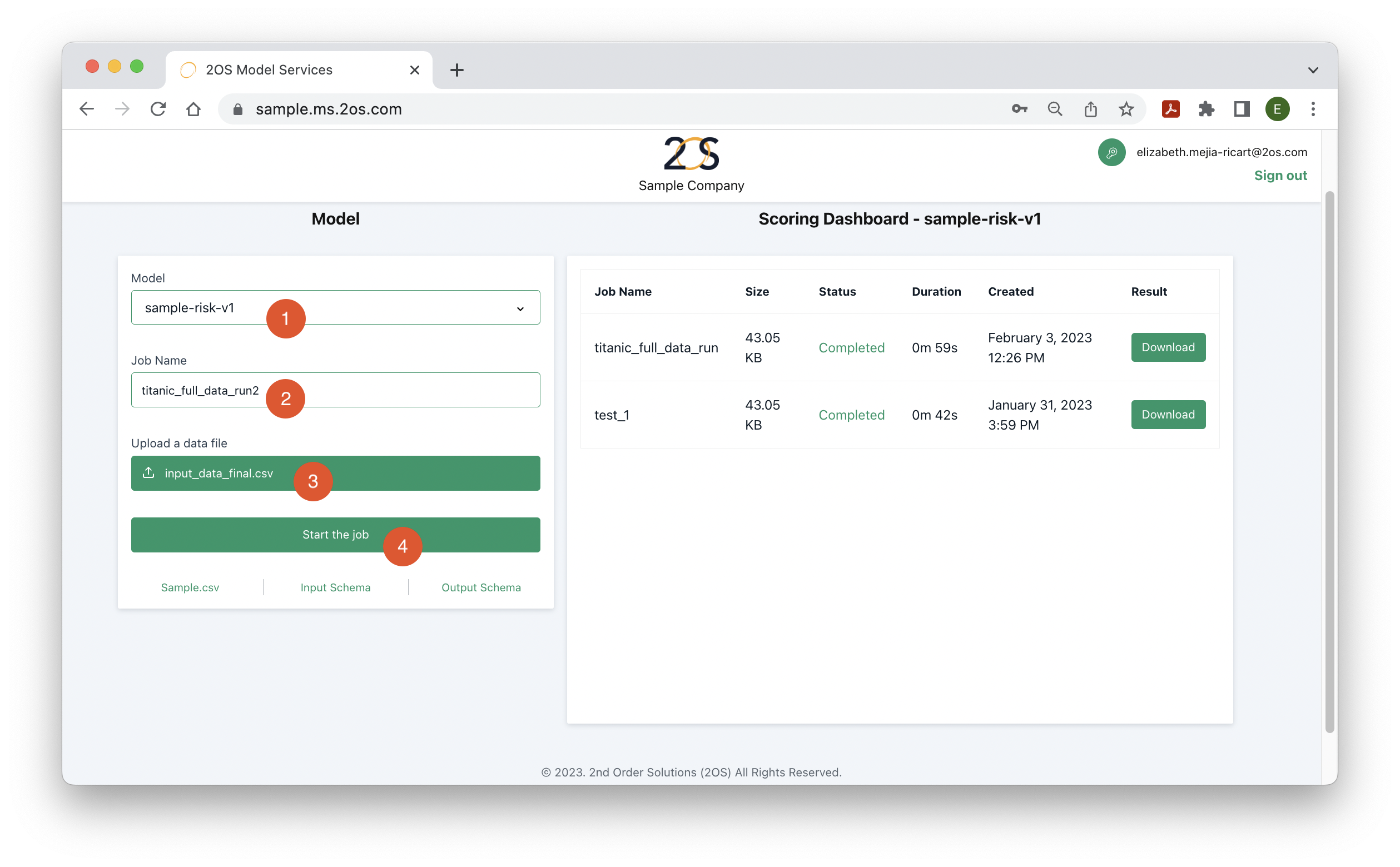
Step 2: Specify the appropriate model and input data
Once logged into the client-specific website, several settings must be specified:
- Model name: Model service allows the deployment of multiple ML models, which can be newer versions of existing models, or could be used in different parts of your credit process. For example, the 2OS team could deploy 2 client-specific models, a risk model for acquisitions and a probability of default model for collections. Select the model that corresponds to the input dataset to be uploaded to the model service webpage.
- Job name: Any descriptive name for the current run should be provided. For example: a name could be provided based on the date of the run or the number of customers scored in the input file. The purpose of this field is to recognize the details of the input file and model from the job name.
- Data file: In this field, the input data (in csv format) is uploaded. It should only have the necessary features for the model to generate a strategy for each customer in the file. More details about the precise format of the data file will be provided in the next section.
- Start the job: After this button is clicked, the model starts transforming the input dataset into the desired response. In the case of a risk model, each customer in the data file will be assigned a risk probability. More details on the output file format will be provided in the coming sections.
Step 3: Understand the Input File
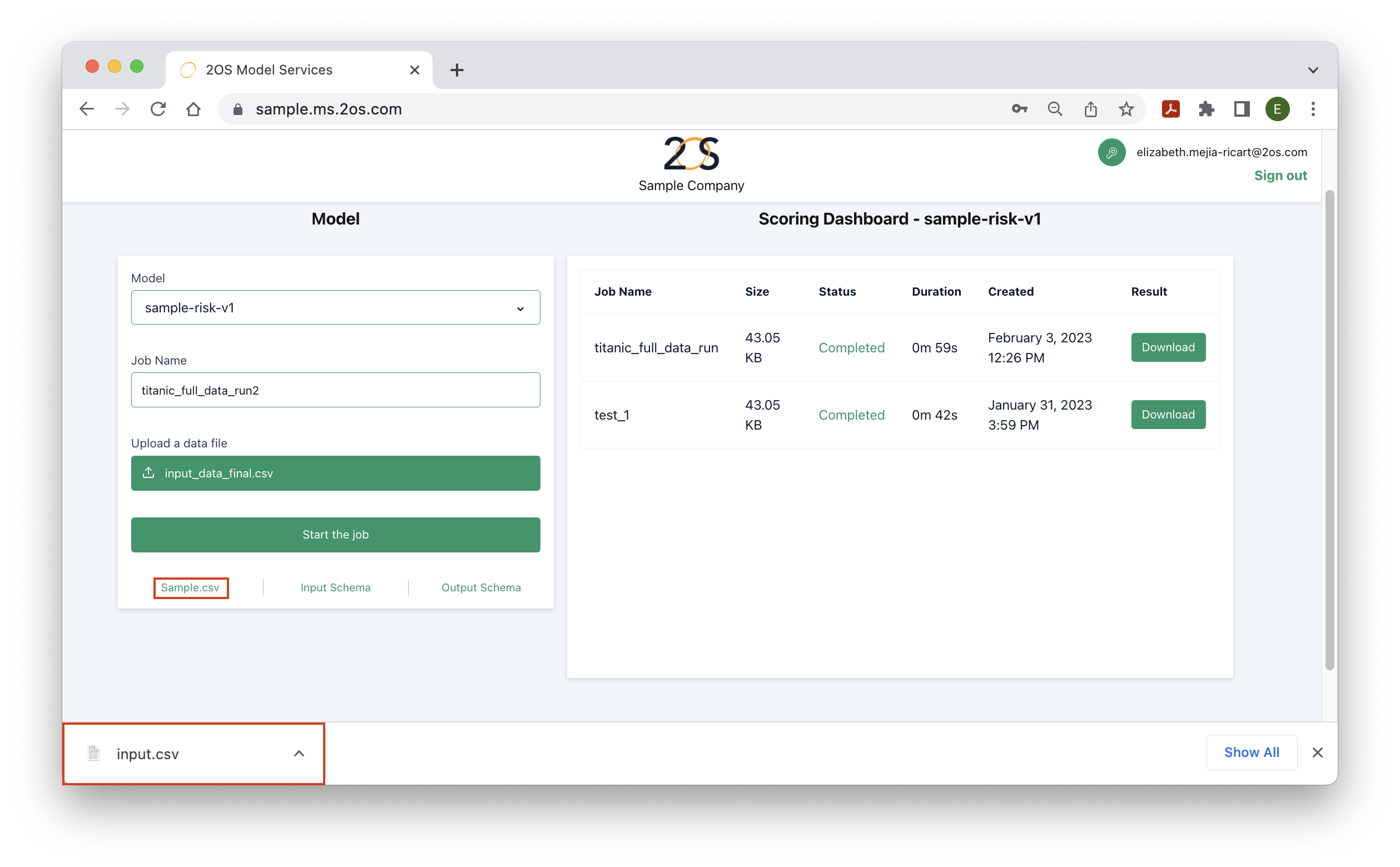
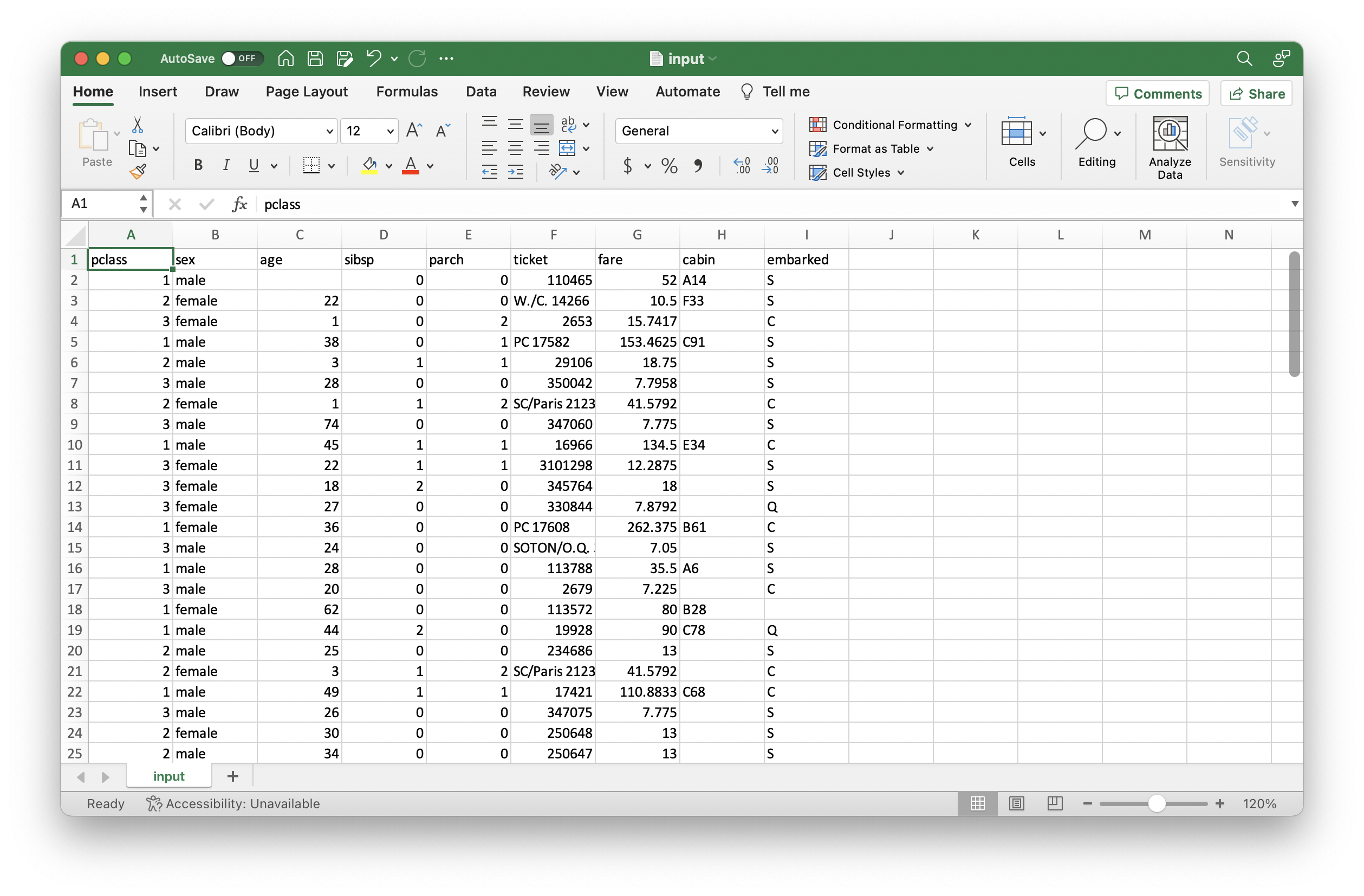
To view the format required for the input file, click on ‘Sample.csv’, as it is indicated in the image below. In a few moments, a csv file (input.csv) with a sample input should have downloaded.
Open the csv file, and notice the feature names and data types required for your input dataset by looking at this sample dataset. Typically, these features are the necessary variables to produce a model score, credit policy or other strategy. In our demo, for example, we use features from the generic titanic dataset to score the probability of survival of a given passenger. Hence, each column consists of features such as which class they travelled in (1st, 2nd, 3rd), sex, gender, etc. for each passenger. Note that the correct number of features, feature names and data types must be provided to get a valid output.
Step 4: Understand the Output File
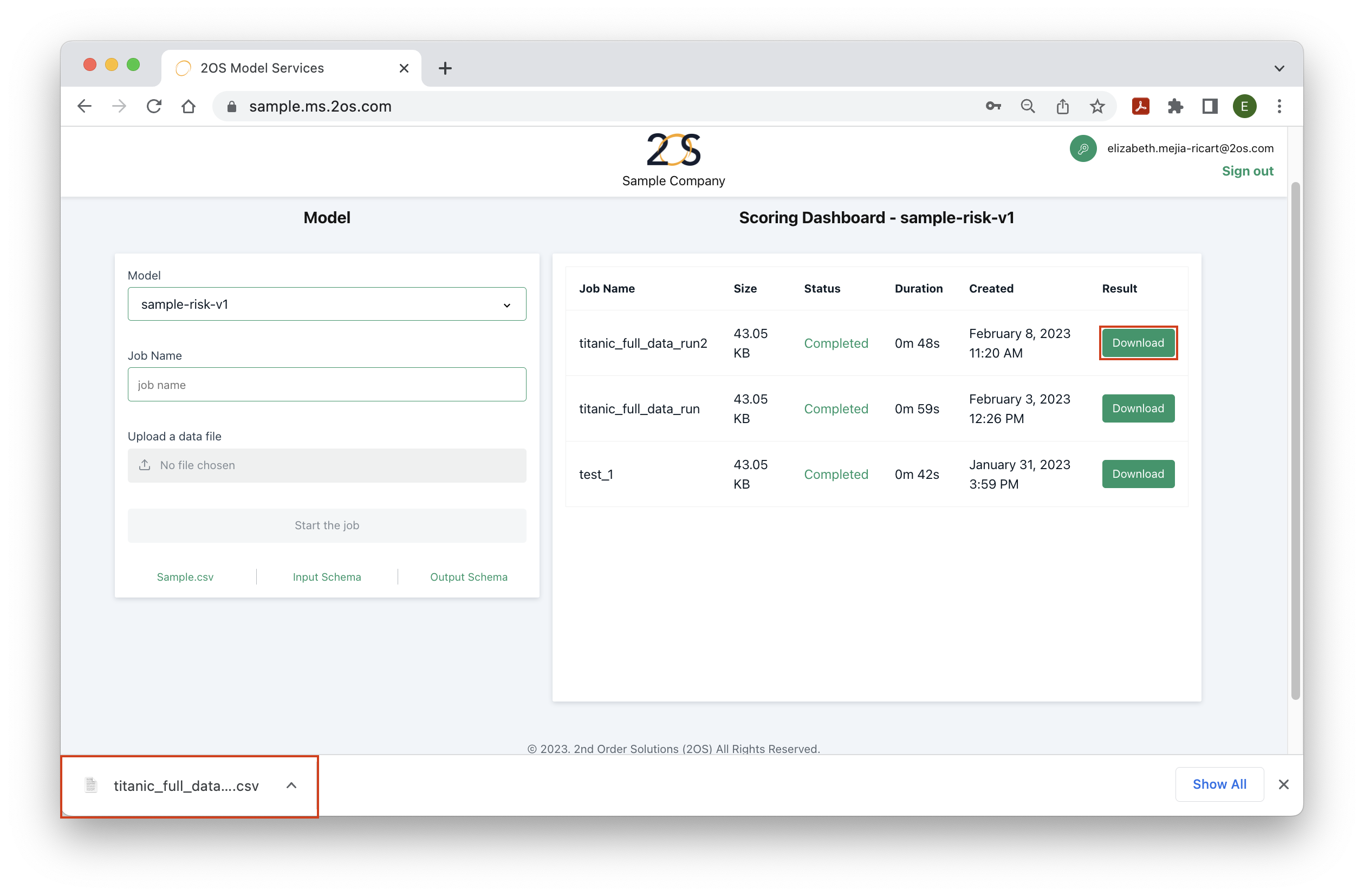
After following the instructions from step 2, the scoring dashboard should provide information about the current run status. Once the job has completed, the ‘Result’ column should give the option to download a file. Click ‘Download’, as it is shown in the image below, to obtain the desired output for your input dataset. Immediately, this output will be downloaded as a csv file.
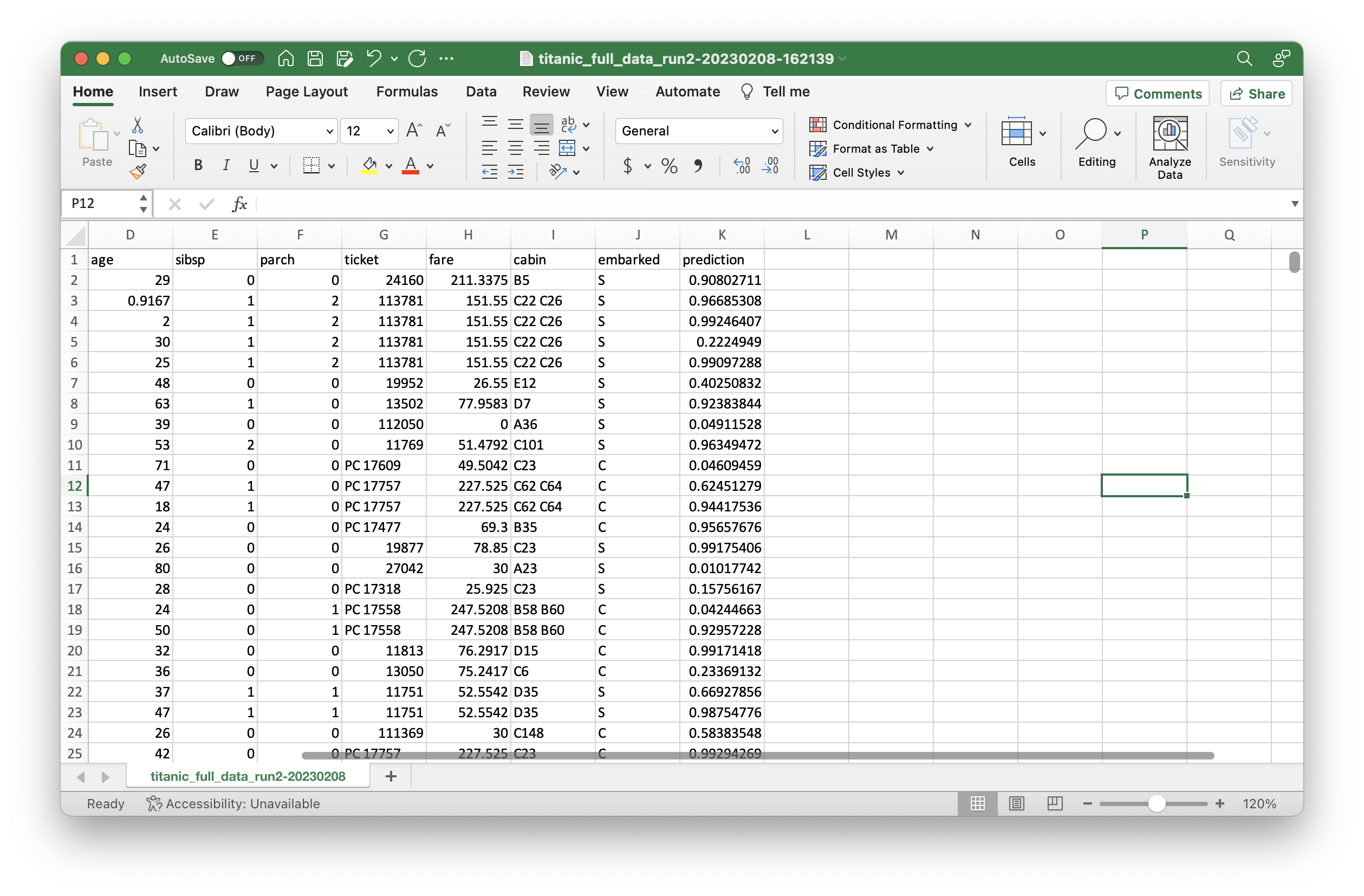
Once the output file is opened, notice that it looks like the input file with one or more columns added. In our demo, we added one column corresponding to the probability of survival of each passenger. The output is adjustable to your needs. In the past, we have produced outputs that specify the risk score, and the recommended loan amount, term and APR structure for each customer.
FAQ
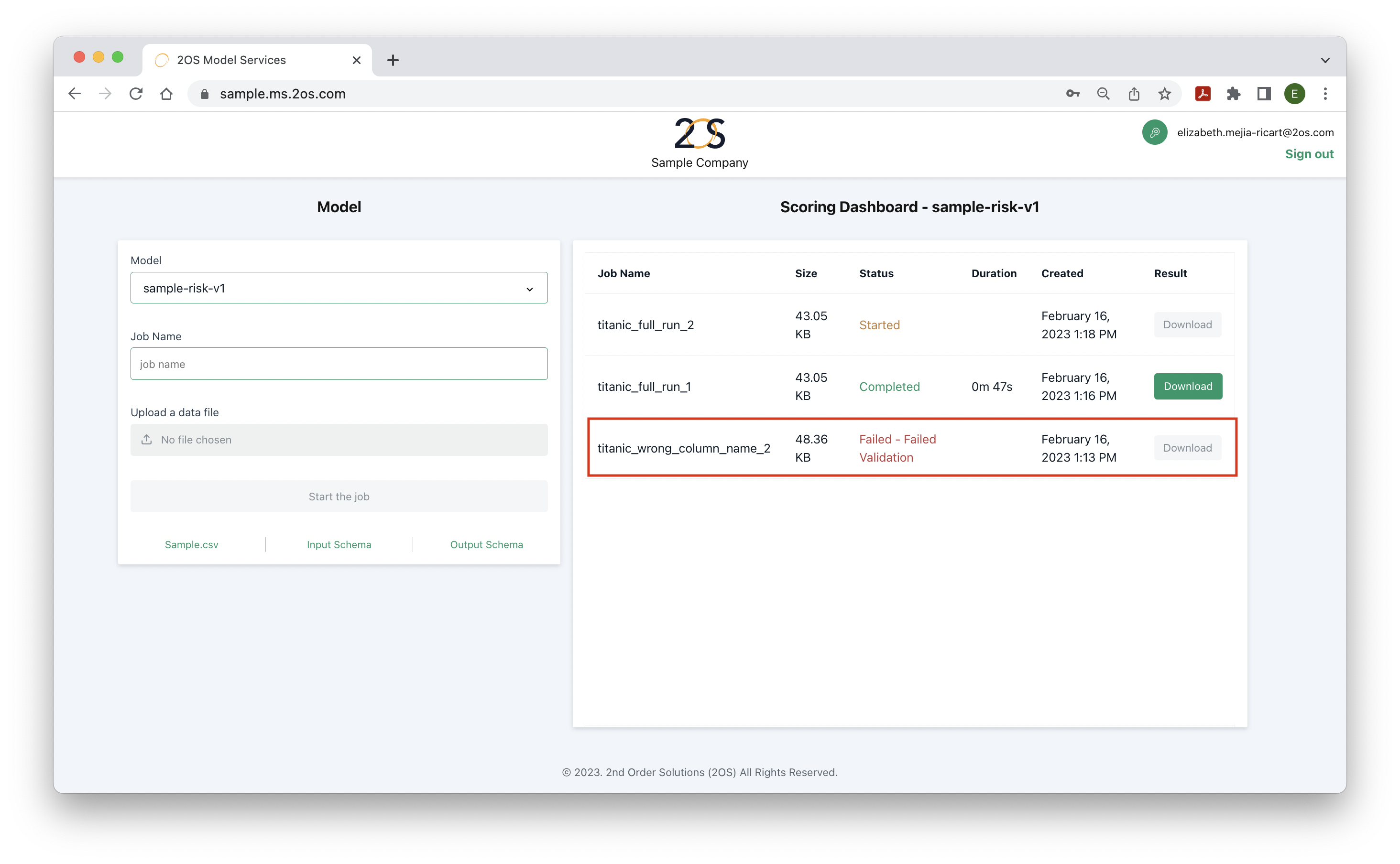
What are each of the scoring dashboard columns?
The scoring dashboard contains information the history of jobs started. Each run should have a unique model, input data and date combination. There are 6 columns in the dashboard:
- Job name: Indicates the name used at the time of the run.
- Size: The size of the input file provided at the time of the run. There are file size limits which should be provided by the 2OS team. Note that the limits are reduced based on the internet speed.
- Status: One of the following: in-processing, completed, failed. Once a job is started, the status column will typically indicate ‘started’, i.e., the input data is being transformed into the output by the deployed model. If Model Service is able to transform the input data successfully, the status will switch to ‘completed’. If the status indicates ‘failed’ or some variation of this, then Model Service was not able to successfully transform the input data into recommended strategies. More details are provided in the next FAQ.
- Duration: The time taken from the time the job was started until it successfully transformed the input data to the output.
- Result: If the job succeeds, a ‘Download’ button will be displayed here to obtain the output.

What are some typical errors?
Under the status column, it is possible for the job to display a ‘failed’ message in some circumstances. These are the most common ones:
- Data types: The input file contains entries with different data types than those accepted by each column. To prevent errors of this type, make sure to understand the data types required by each column, by looking at the sample csv in the website. For more information, contact a 2OS team member.
- Number of columns: Model service requires to provide the exact number of variables specified in the sample csv. Providing more or less variables than necessary will cause an error.
- Column names: It is important to provide the exact column names specified in the sample csv.
- Index column: Sometimes, when editing datasets in Python, an index column is generated automatically. Uploading a dataset with that extra index column will result in an error. Make sure to delete the index column before saving and uploading the input dataset.